Causative gene for new motor neuron disease identified Discovery may lead to elucidation of disease mechanisms

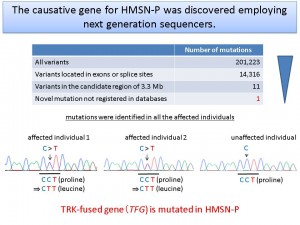
The causative gene for HMSN-P was discovered employing next generation sequencers. © Hiroyuki Ishiura
Hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with proximal dominant involvement (HMSN-P) is a hereditary motor neuron disease that has predominantly been observed in Japan. The clinical presentations of HMSN-P are characterized by the age at onset in adulthood and muscular weakness involving predominantly proximal muscles. Although sensory disturbances are occasionally observed in advanced stages, the primary abnormality is progressive degeneration of motor neurons quite similar to that in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The causative gene for HMSN-P has been discovered by a collaborative team of the University of Tokyo (Prof. Shoji Tsuji) and Tokushima University (Prof. Ryuji Kaji), employing next generation sequencers. Furthermore, the mechanisms of motor neuron degeneration in HMSN-P have been identified to share many aspects with those in ALS. The present findings are expected to contribute to understanding not only mechanisms of motor neuron degeneration in HMSN-P but also those in ALS.
Press release (Japanese)Paper
Hiroyuki Ishiura, Wataru Sako, Mari Yoshida, Toshitaka Kawarai, Osamu Tanabe, Jun Goto, Yuji Takahashi, Hidetoshi Date, Jun Mitsui, Budrul Ahsan, Yaeko Ichikawa, Atsushi Iwata, Hiide Yoshino, Yuishin Izumi, Koji Fujita, Kouji Maeda, Satoshi Goto, Hidetaka Koizumi, Ryoma Morigaki, Masako Ikemura, Naoko Yamauchi, Shigeo Murayama, Garth A. Nicholson, Hidefumi Ito, Gen Sobue, Masanori Nakagawa, Ryuji Kaji, Shoji Tsuji,
“The TRK-fused gene is mutated in hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy with proximal dominant involvement (HMSN-P).”
The American Journal of Human Genetics Volume 91, Issue 2, 320-329, 10 August 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.07.014.
Article link