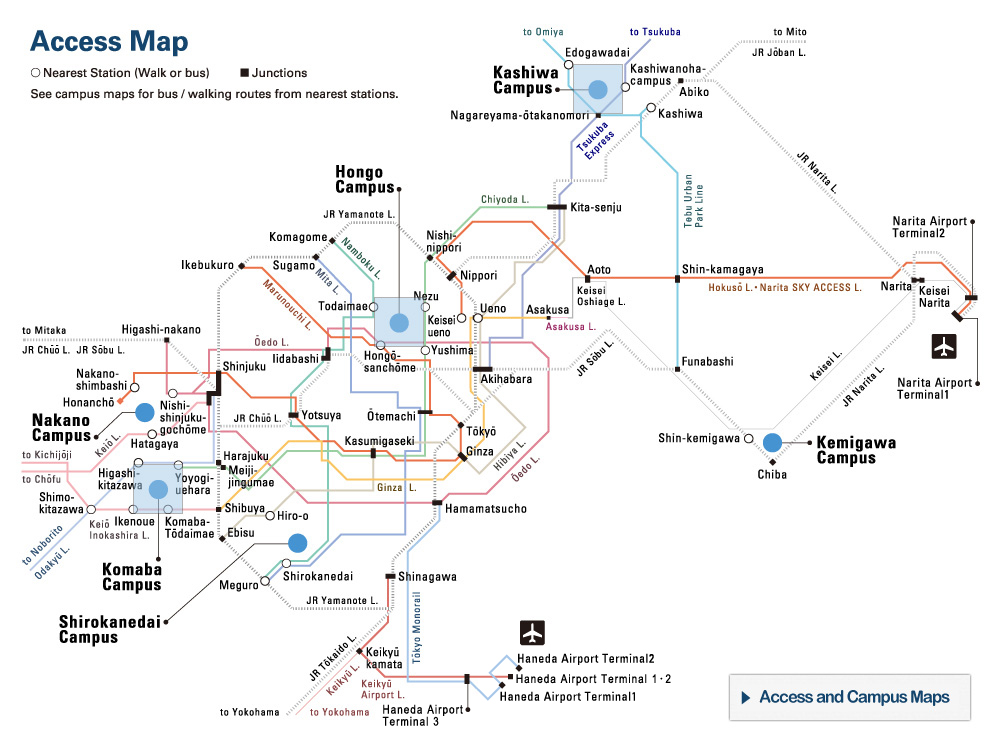
Dual-ion battery A new, inexpensive rechargeable battery

New battery technologies, with energy density greater than current lithium ion batteries, are urgently needed for use in electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles and for the exploitation of new energy resources such as solar and wind power. Such batteries should be inexpensive and highly safe in addition to this basic functionality.
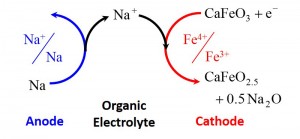
© Noritaka Mizuno. A new rechargeable battery utilizing reversible topotactic oxygen extraction/insertion between iron-based CaFeOz (2.5 ≤ z ≤ 3) in organic electrolyte with sodium anode.
Professor Noritaka Mizuno at Department of Applied Chemistry of the University of Tokyo and his research group are engaged in research to develop a new type of battery that overcomes some problems that conventional batteries face, and have demonstrated a rechargeable “Oxygen Shuttle battery (Oxygen Rocking battery).” While this “Oxygen Shuttle battery” is extremely safe, energy density was not high enough.
In their latest research, the group have successfully demonstrated a “Dual-ion battery” using a calcium iron(IV) oxide (CaFeO3) cathode, sodium ion (Na+) electrolyte and metallic sodium (Na) anode.
In this new type of battery system contains two mobile ions, an oxide ion present in the cathode material and an electrolyte ion matched with the anode material, leading to its “dual-ion” name. In addition to the sodium ion electrolyte demonstrated in the current research, lithium or other ion electrolytes can be used, meaning that lithium or sodium can be used as the anode for the same cathode. This removes the need to search for suitable cathode materials as in the case of conventional lithium or sodium ion batteries. Further, it is possible to use cathode materials that do not contain scarce elements, such as CaFeO3 used in this research, removing the need for expensive and toxic compounds such as cobalt used in the conventional lithium ion batteries.
This research is supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) through its “Funding Program for World-Leading Innovative R&D on Science and Technology (FIRST Program)”.
Paper
M. Hibino, R. Harimoto, Y. Ogasawara, R. Kido, A. Sugahara, T. Kudo, E. Tochigi, N. Shibata, Y. Ikuhara, N. Mizuno,
“A New Rechargeable Sodium Battery Utilizing Reversible Topotactic Oxygen Extraction/Insertion of CaFeOz (2.5 ≤ z ≤ 3) in An Organic Electrolyte,”
Journal of the American Chemical Society 136, 488-494 (2014), doi: 10.1021/ja411365z.
Article link
Links
Graduate School of Engineering
Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering
Mizuno Lab, Department of Applied Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering
FIRST program ? Innovative Basic Research Toward Creation of High-performance Battery