The genetics of early-onset gout Dysfunctional variants of urate exporter gene strongly correlated

Gout is a common disease resulting from elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, the symptoms of which include agonizing joint pain. Patients are also at increased risk of high blood pressure and strokes. Gout is most prevalent in males after middle age, but more people nowadays develop it before the age of thirty.
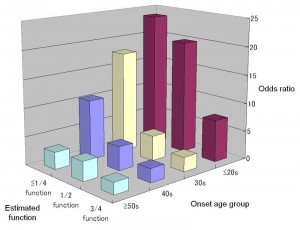
It is known that ABCG2, a high-capacity urate transporter which regulates serum (blood) uric acid levels, is a major cause of gout. A research team including Research Associate Hirotaka Matsuo and Medical Officer Akiyoshi Nakayama of the National Defense Medical College, Professor Kimiyoshi Ichida of the Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, and Research Associate Tappei Takada of the University of Tokyo Hospital’s Department of Pharmacy, investigated whether common dysfunction of ABCG2 is also associated with early-onset gout. 705 Japanese male gout cases with onset age data and 1,887 male controls were genotyped, and the ABCG2 functions which are estimated by its genotype combination were determined. The onset age was 6.5 years earlier with severe ABCG2 dysfunction than with normal ABCG2 function (P = 6.14 × 10-3). Patients with mild to severe ABCG2 dysfunction accounted for 88.2% of early-onset cases (less than thirty years old). Severe ABCG2 dysfunction was associated with a more than twenty-fold increase in the risk of early-onset gout (odds ratio 22.2, P = 4.66 × 10-6).
The test for mutation of the gene encoding ABCG2 is relatively easy to perform and may be a useful means of establishing risk of early-onset gout. By continuous management of health from a young age and in addition to preventing the development of gout, it may also be possible to prevent associated problems such as high blood pressure and strokes, enabling the long-term maintenance of health and improve quality of life while reducing medical costs. This research was published online in the journal Scientific Reports on 18 June 2013 (Japan time).
Press release (Japanese)
Paper
Matsuo H, Ichida K, Takada T, Nakayama A, Nakashima H, Nakamura T, Kawamura Y, Takada Y, Yamamoto K, Inoue H, Oikawa Y, Naito M, Hishida A, Wakai K, Okada C, Shimizu S, Sakiyama M, Chiba T, Ogata H, Niwa K, Hosoyamada M, Mori A, Hamajima N, Suzuki H, Kanai Y, Sakurai Y, Hosoya T, Shimizu T, Shinomiya N,
“Common dysfunctional variants in ABCG2 are a major cause of early-onset gout”,
Scientific Reports 3 2013: 2014, doi: 10.1038/srep02014.
Article link