Identification of extra-cellular protein Notch as cause of osteoarthritis Novel finding should lead to breakthrough in treatment of osteoarthritis

Osteoarthritis of the knee is a disease that causes friction in the knee joint and greatly lowers the quality life of the elderly, reduces life expectancy, and is the principle disease of what the Japanese Orthopaedic Association terms “locomotive syndrome.” However, there is no current treatment that addresses the underlying causes of the disease. Accumulated evidence has identified several molecules as potential triggers of osteoarthritis of the knee, but these were all intracellular molecules and difficult therapeutic targets for drug-delivery systems.
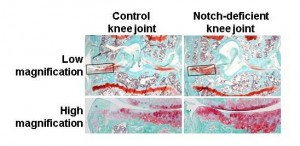
There was clear degradation of cartilage matrix (red area) in the control group (left), which is prevented by knockout of Notch signaling (right). © Hiroshi Kawaguchi
In this research, graduate student Yoko Hosaka, Associate Professor Hiroshi Kawaguchi and their colleagues at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery in the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Medicine, used mouse experiments to identify Notch, a membrane receptor in chondrocytes, cells which maintain the structure of cartilage, as a novel molecule controlling osteoarthritis development. Intra-articular injection of a small compound DAPT, a Notch inhibitor, prevented osteoarthritis in a mouse model. As Notch is an extracellular protein, it provides a much more accessible target for treatment. Modulation of Notch signaling, for example by injecting DAPT, may lead to a breakthrough in the disease-modifying treatment of osteoarthritis.
Press release (Japanese)
Paper
Yoko Hosaka, Taku Saito, Shurei Sugita, Tomohiro Hikata, Hiroshi Kobayashi, Atsushi Fukai, Yuki Taniguchi, Makoto Hirata, Haruhiko Akiyama, Ung-il Chung, Hiroshi Kawaguchi
“Notch signaling in chondrocytes modulates endochondral ossification and osteoarthritis development”,
PNAS Online Edition: 2013/1/15, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207458110.
Article link
Links
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Spinal Surgery, University of Tokyo Hospital (Japanese)