Deep sulfur cycle involving atmosphere, ocean and mantle Precise model of sulfur circulation developed

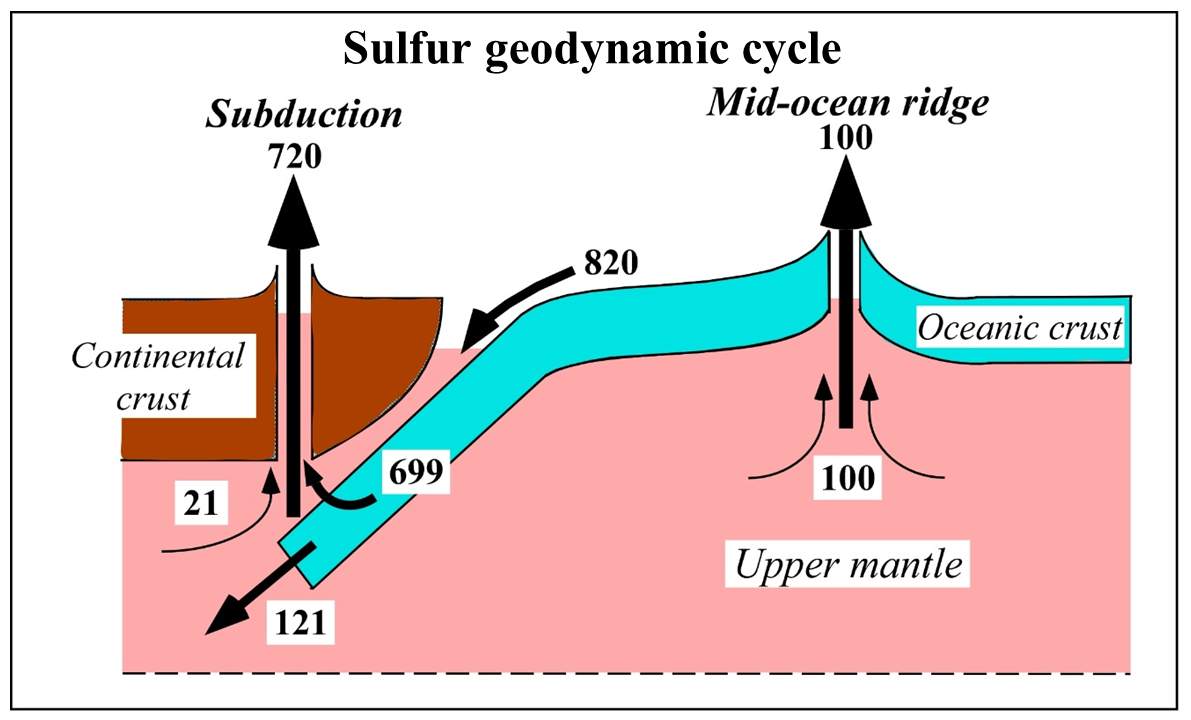
Graduate student Takanori Kagoshima and Professor Yuji Sano at the University of Tokyo’s Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute have constructed a detailed model of the global sulfur cycle including the Earth’s deep mantle.
Sulfur is an important element incorporated in living organisms, and is also an important ingredient of synthetic fibers and medicines. However, its geochemical cycle between the mantle and surface environments had not been sufficiently quantified. The research group calculated sulfur flux from the mantle to atmosphere and ocean based on precise analyses of mid-ocean ridge basalt, which is derived from the mantle and has the same chemical composition (basaltic igneous rocks from the submarine volcanic group where ocean floor is continuously being created), and data analysis of submarine hydrothermal fluid and volcanic gases worldwide. In addition, they calculated sulfur amounts recycled back into the deep mantle based on the mass-balance of sulfur in surface environments, and constructed a detailed model of the global sulfur cycle.
This study provides a model of the global deep sulfur cycle of unprecedented precision and complements material cycles in surface environments. This result will be highly important for revealing the process of the Earth’s evolution.
Press release (Japanese)
Paper
, "Sulphur geodynamic cycle", Scientific Reports Online Edition: 2015/2/9 (Japan time), doi: 10.1038/srep08330.
Article link (Publication, UTokyo Repository)
Links
Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute
Department of Chemical Oceanography, Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute