Targeted therapy of intractable pancreatic cancer in transgenic mice Proof of efficacy of nanoscale drug delivery system

Recently, nanoscale drug delivery systems (DDS) for targeted cancer therapy have been attracting much attention, as they enable the targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs directly to the cancer itself, enabling excellent clinical outcomes without damaging side-effects. Nevertheless, most such studies have been performed against inoculated tumor models, where a tumor is induced in the host. Studies using more clinically relevant naturally-occurring tumors are important to translate these experimental results into clinical practice.
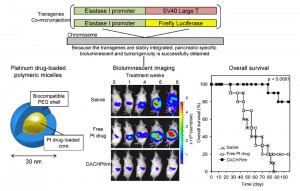
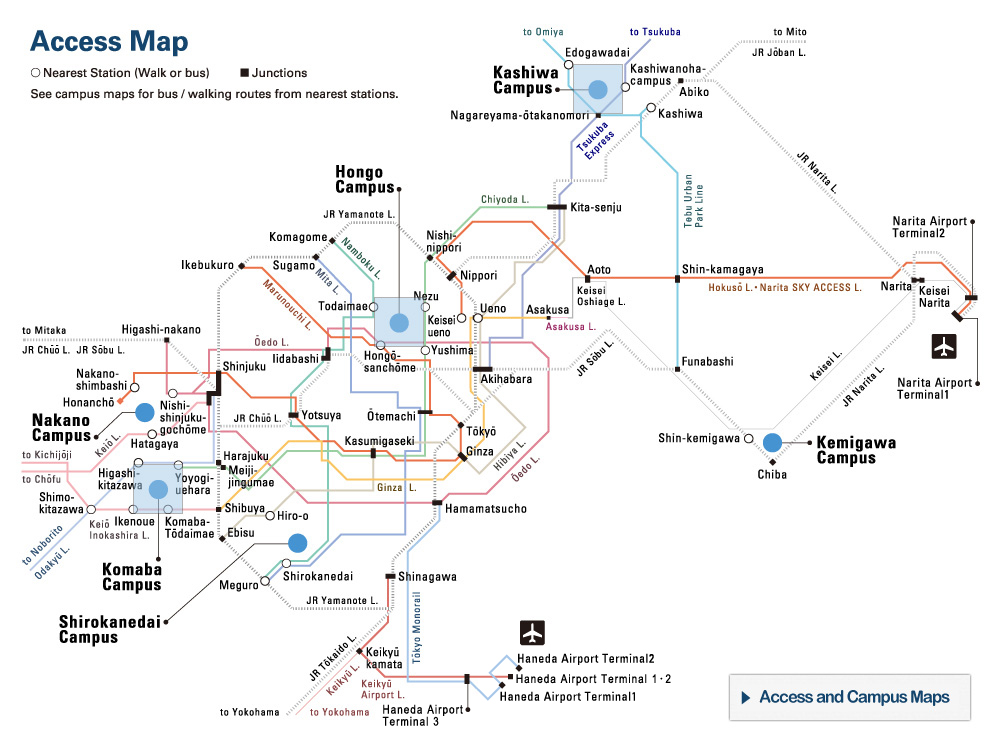
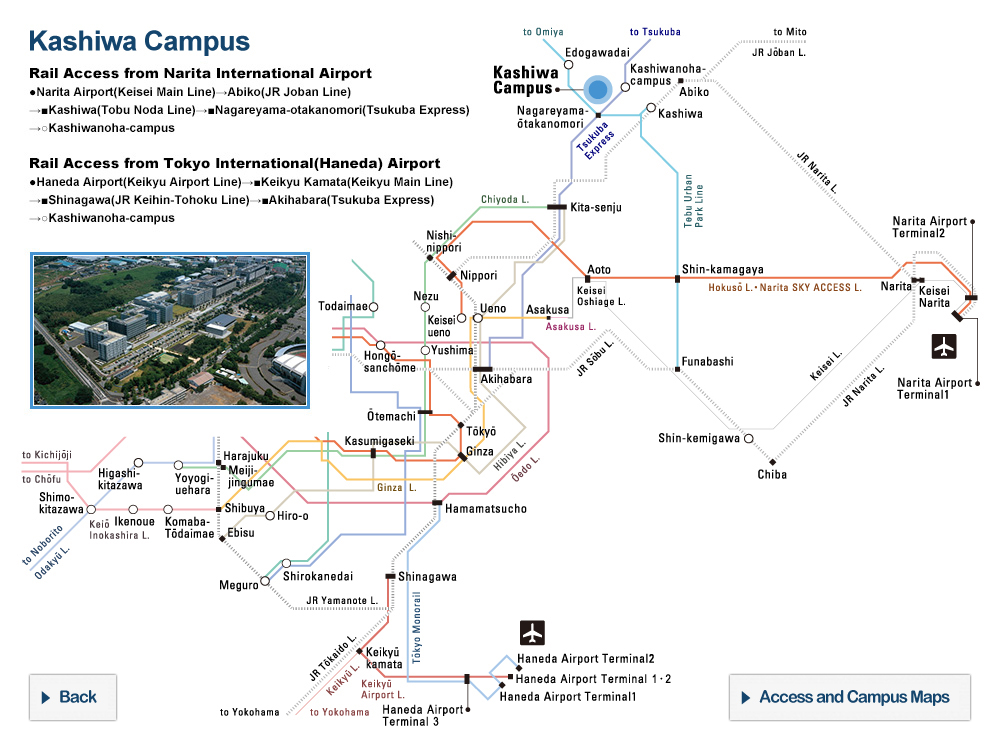
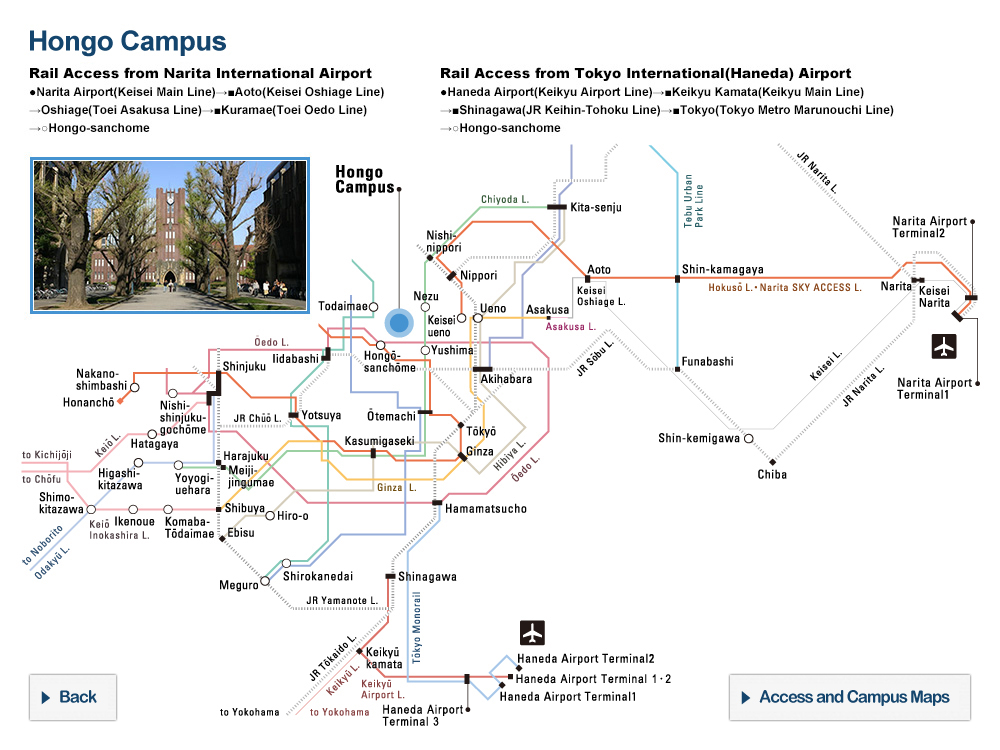
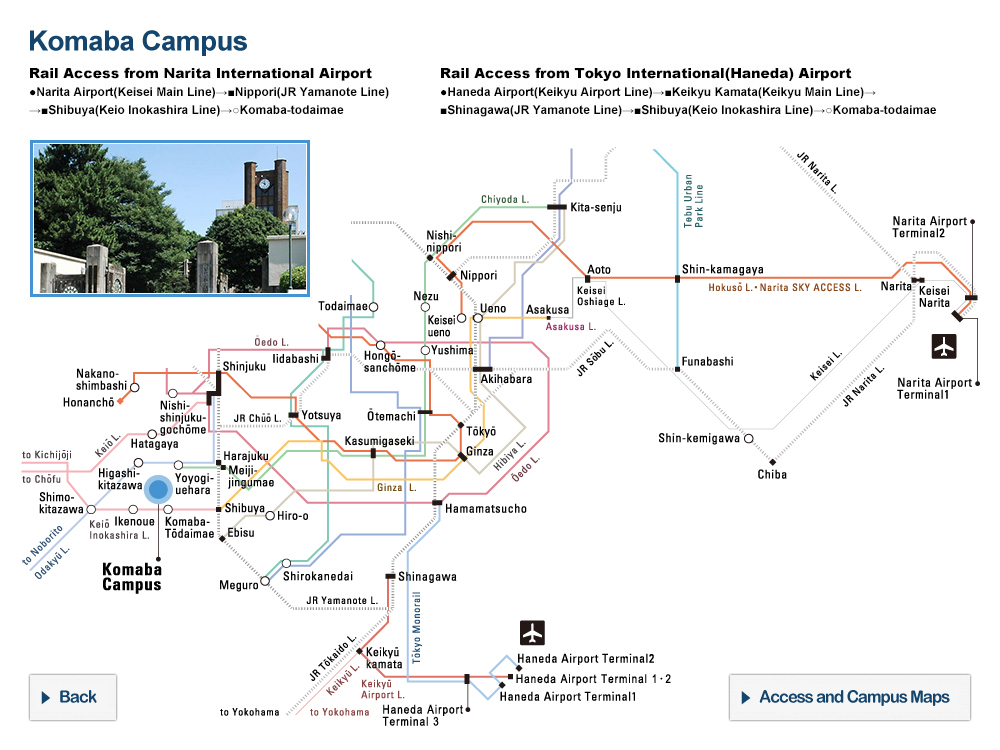
© Cabral Horacio et al., (Left) Image of a platinous anti-cancer drug encapsulated in a polymeric micelle, (center) extent of cancer in transgenic mice that develop spontaneous pancreatic cancer treated with saline, unencapsulated free drug, and encapsulated drug, and (right) survival rates for mice under each treatment.
In this study, Professor Kazunori Kataoka’s research group in the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Engineering and Graduate School of Medicine has studied the efficacy of DDS based on polymeric micelles, a self-assembled capsule composed of synthetic block copolymers, by using a strain of transgenic mice that spontaneously develops pancreatic cancer. As a result, polymeric micelles incorporating a platinous anticancer agent showed enhanced tumor accumulation and remarkable anticancer effects in the spontaneous pancreatic cancer model, extending the survival of the transgenic mice.
Pancreatic cancer is known as the most intractable cancer with the lowest 5-year survival rate and no effective treatments available. It is hoped that this research will lead to the development of an effective treatment for pancreatic cancer based on the use of polymeric micelles.
Press release [pdf] (Japanese)
Paper
Horacio Cabral, Mami Murakami, Hironori Hojo, Yasuko Terada, Mitsunobu R. Kano, Ung-il Chung, Nobuhiro Nishiyama, Kazunori Kataoka,
“Targeted therapy of spontaneous murine pancreatic tumors by polymeric micelles prolongs survival and prevents peritoneal metastasis”,
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110 (28) 11397-11402 (2013), doi: 10.1073/pnas.1301348110.
Article link
Links
Graduate School of Engineering
Department of Materials Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering
Center for Disease Biology and Integrative Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine
Kataoka Laboratory, Department of Materials Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering
The University of Tokyo Global COE Center for Medical System Innovation