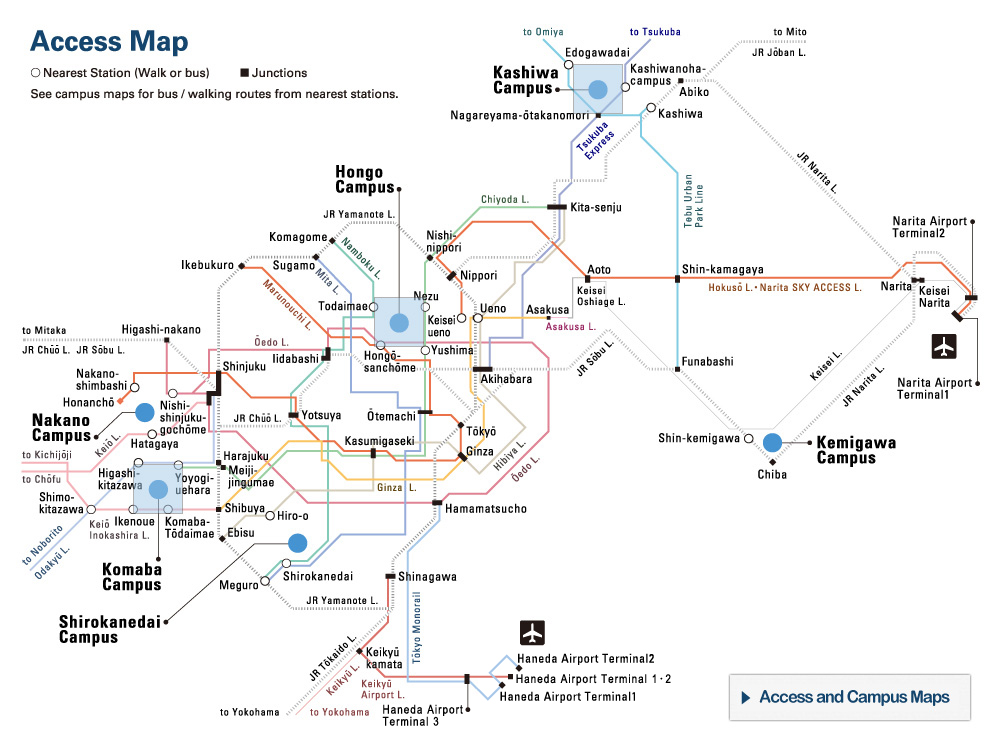
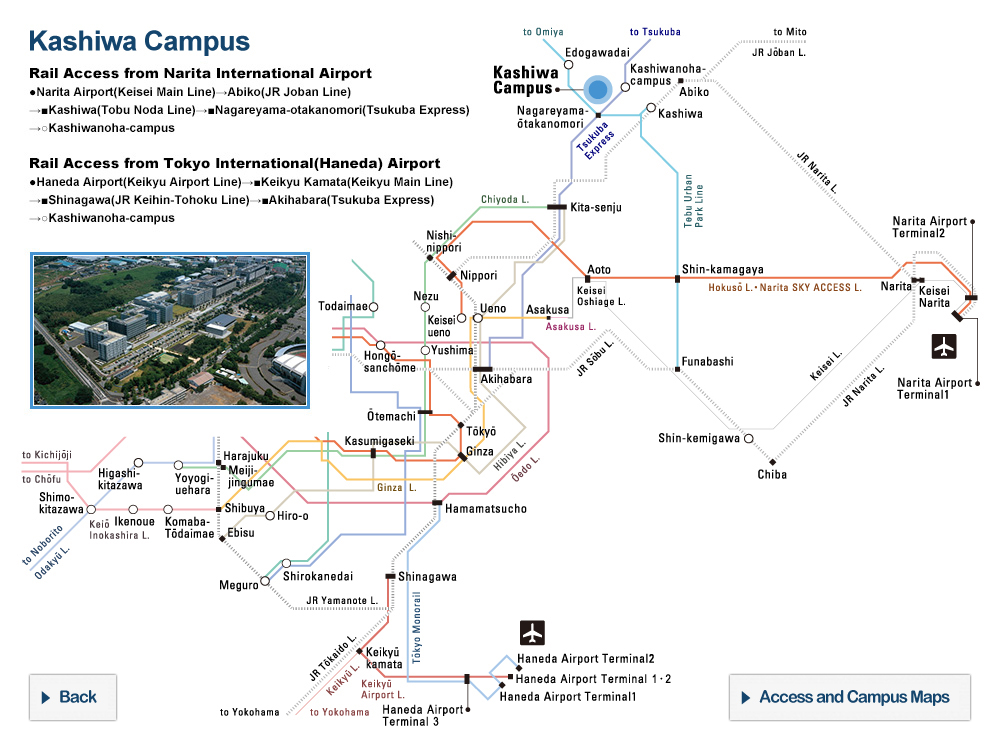
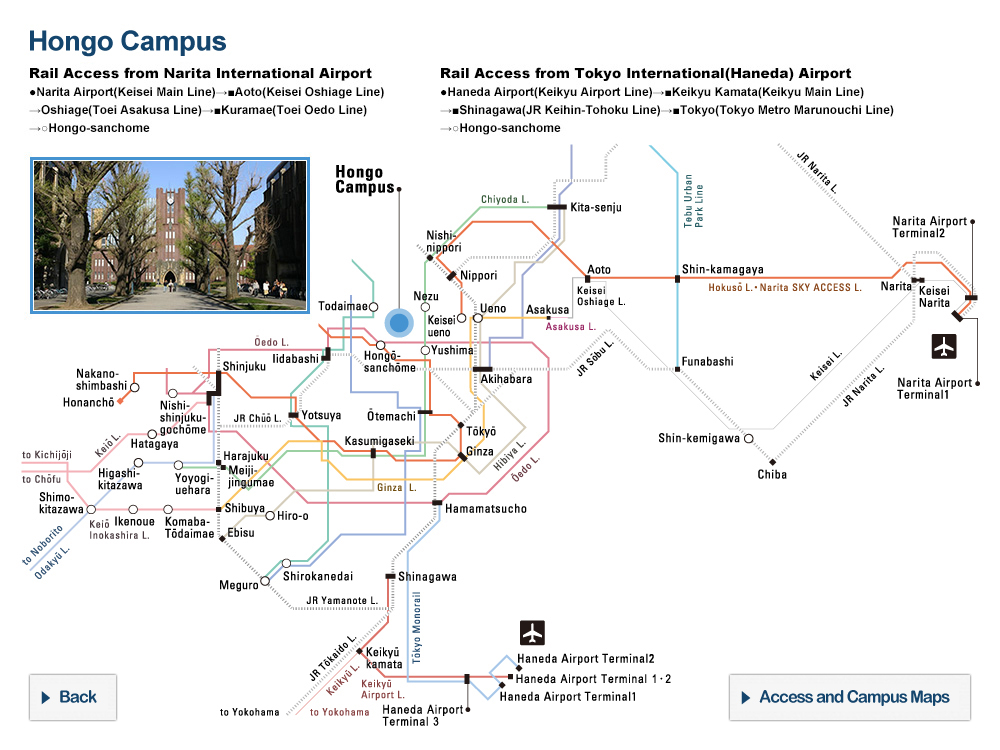
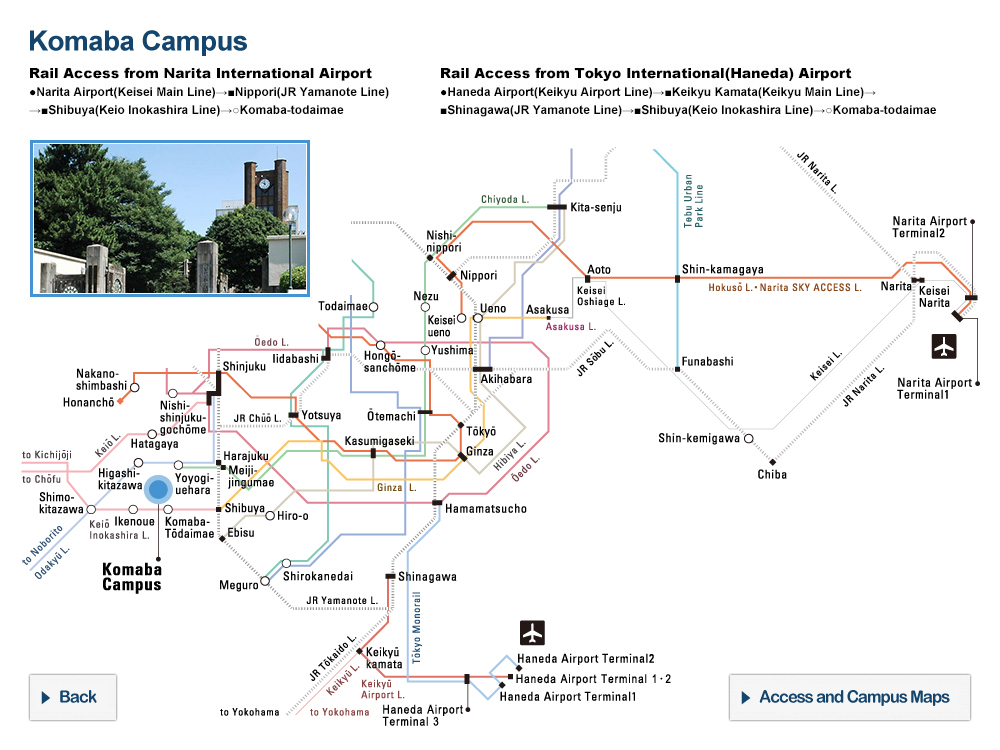
UTokyo, French Geological Survey Sign Agreement for Disaster Risk Reduction Through Muography

Date of activity: October 2, 2017
The University of Tokyo and France’s geological survey, BRGM, signed an agreement on October 2, 2017, to enhance their scientific cooperation to help reduce and manage disaster risks through the imaging technique known as muography.
The technique may remind us of medical imaging, like X-rays, but uses elementary particles originated from outer space called muons to penetrate massive objects spanning several hundred meters, providing us the tools to investigate the inside of volcanoes, caves, and landslides, among other natural phenomena and manmade structures.
France’s Higher Education, Research and Innovation Minister Frédérique Vidal, who attended the signing ceremony at the French Embassy in Tokyo, expressed her high expectations for disciplinary diversity in muographic research to foster personnel exchanges between France and Japan.
The memorandum of understanding between the University of Tokyo’s Earthquake Research Institute (ERI) and the French government agency was signed by ERI Director Kazushige Obara and BRGM Deputy CEO Pierre Toulhoat.
The signing followed the Muographers 2017 general assembly, a full day of presentations by Japanese and European scientists on the uses of muography to gain insights on difficult-to-access structures, organized by the ERI and other Japanese and European institutions.
ERI’s Professor Hiroyuki Tanaka, a principal organizer of Muographers 2017, says, “I hope to see that the community will create a further expansion for leading-edge multidisciplinary research in the world.”
The events kicked off the French-Japanese Week on Disaster Risk Reduction organized by the French Embassy.

ERI Director Kazushige Obara, at left foreground, and BRGM Deputy CEO Pierre Toulhoat clasp hands at an MoU signing ceremony between their institutions, at the French Embassy in Tokyo on October 2. From the right at back, French Higher Education, Research and Innovation Minister Frédérique Vidal, French Ambassador Laurent Pic, Science and Technology Attaché Sébastien Codina, and ERI’s Professor Hiroyuki Tanaka look on. 
Group photo of muographers participating in the MoU signing ceremony at the French Embassy on October 2.