Ancient migration was choice, not chance Paleolithic people likely colonized the Ryukyu Islands intentionally Research news

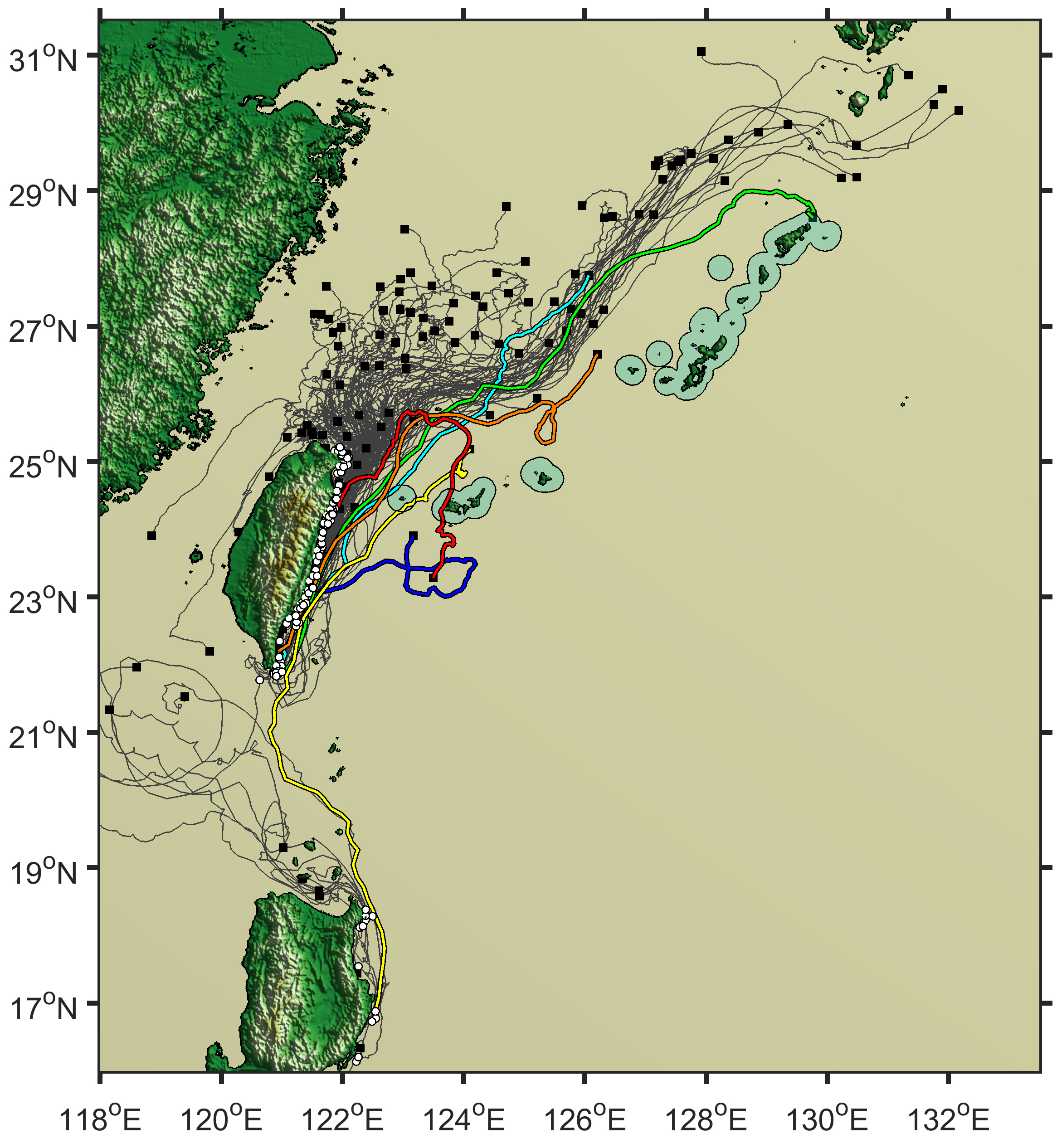
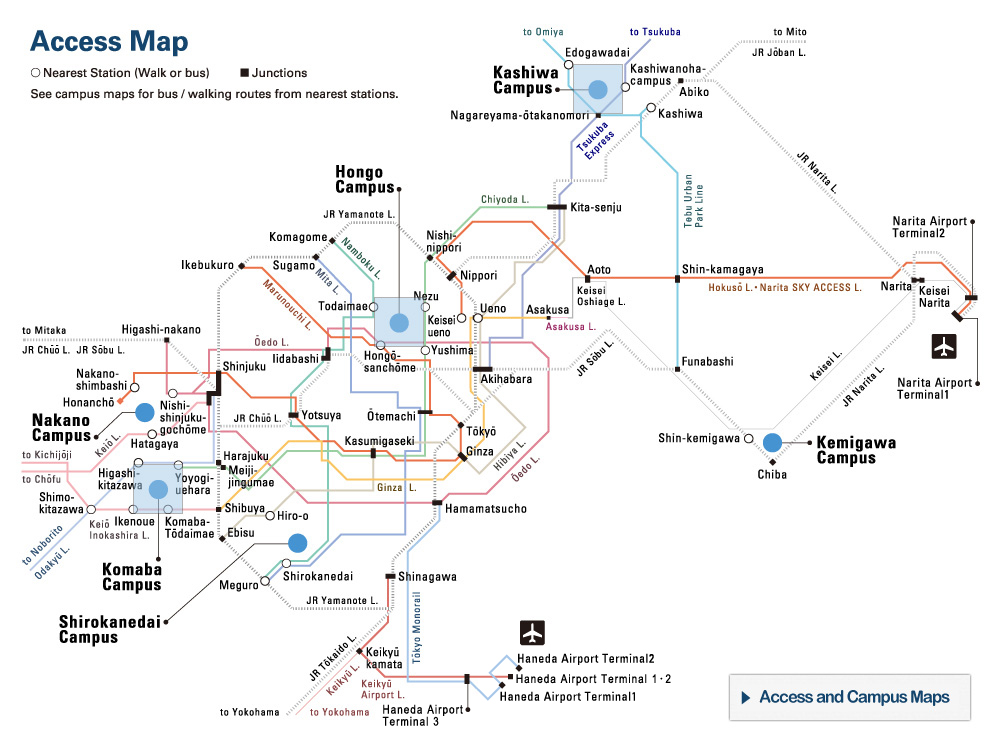
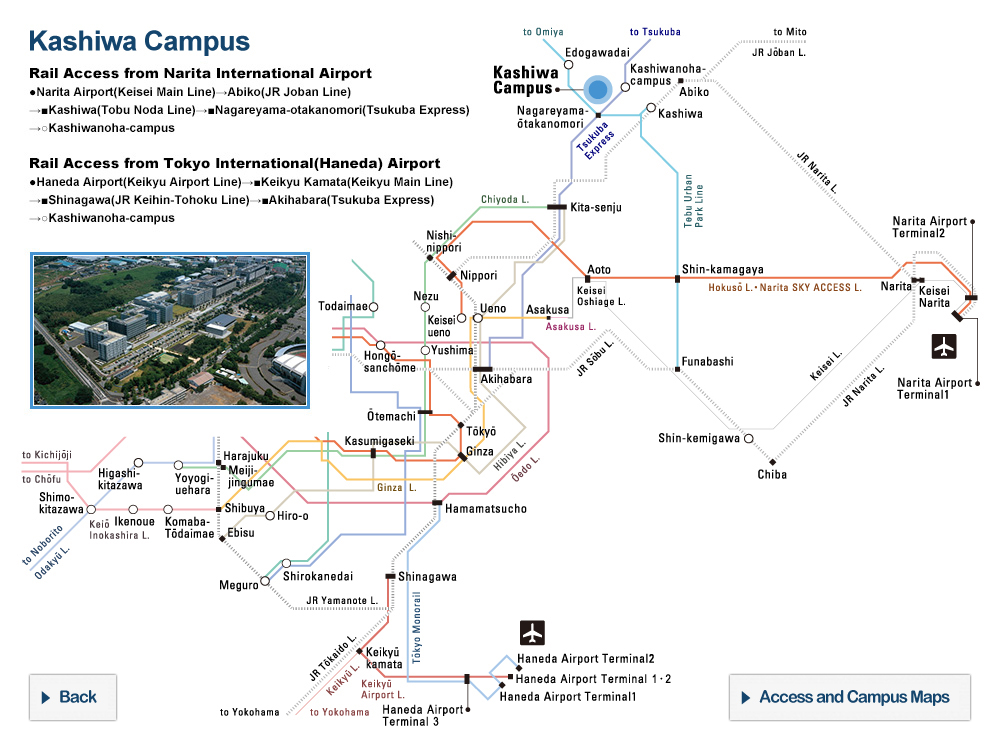
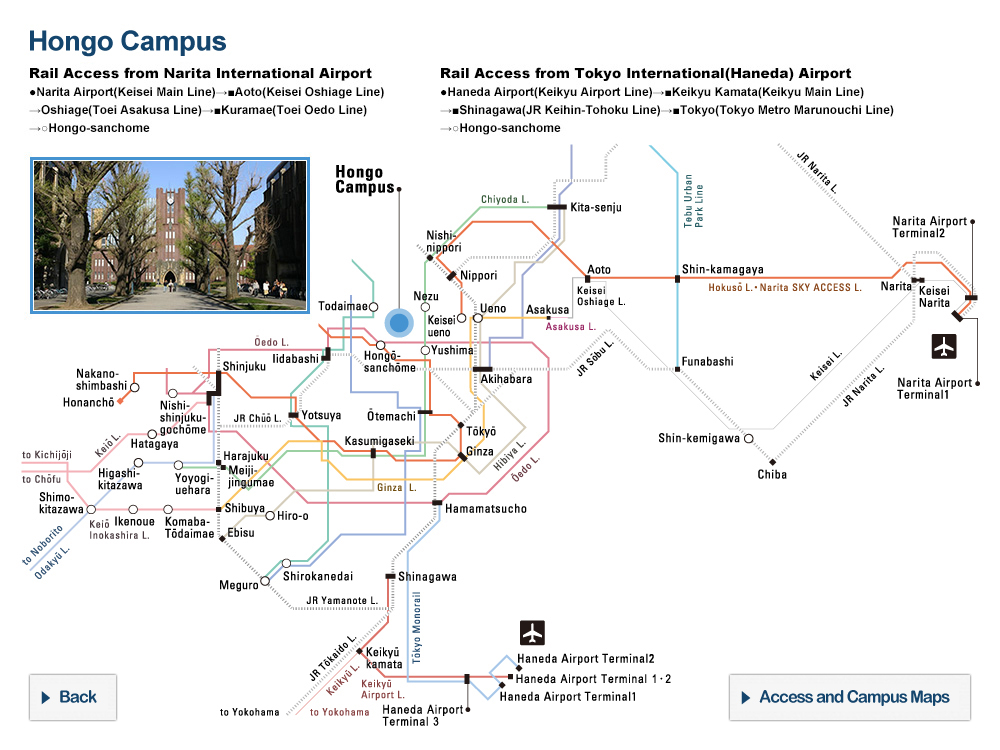
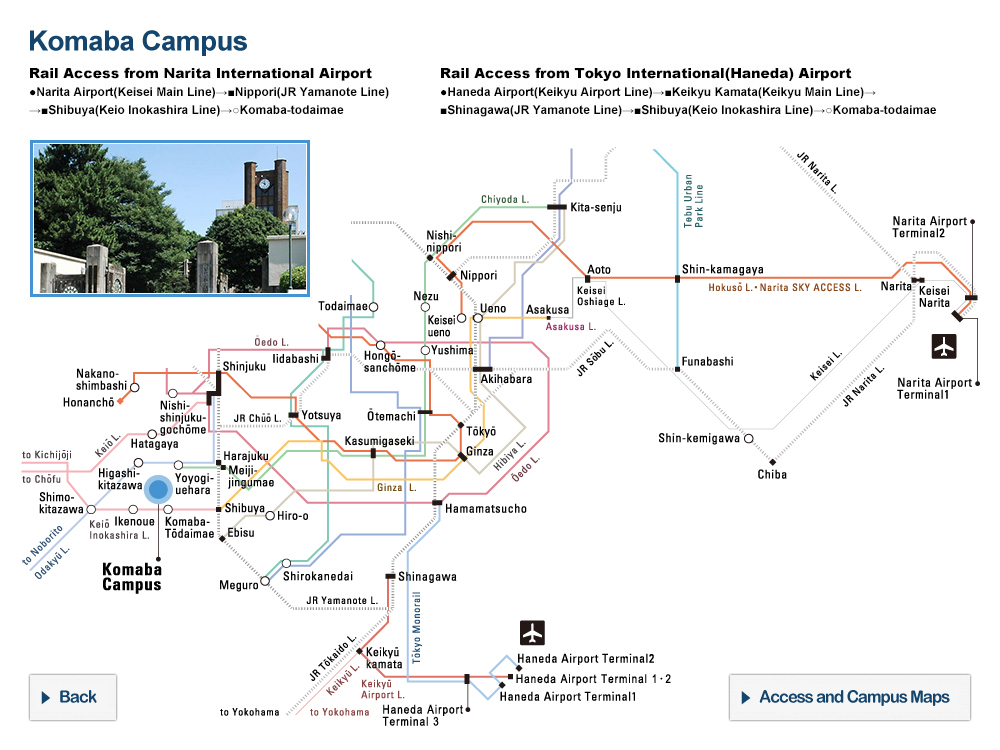
The buoys’ journey. Tracking data for 138 buoys, including several which ventured relatively near the target islands. © 2020 Tien-Hsia Kuo
The degree of intentionality behind ancient ocean migrations, such as that to the Ryukyu Islands between Taiwan and mainland Japan, has been widely debated. Researchers used satellite-tracked buoys to simulate ancient wayward drifters and found that the vast majority failed to make the contested crossing. They concluded that Paleolithic people 35,000-30,000 years ago must therefore have made the journey not by chance but by choice.
Human migration over the last 50,000 years is an essential part of human history. One aspect of this story that fascinates many is the ways in which ancient people must have crossed between separate land masses. Professor Yosuke Kaifu from the University Museum at the University of Tokyo and his team explore this subject, in particular a crossing known to have taken place 35,000-30,000 years ago from Taiwan to the Ryukyu Islands, including Okinawa, in southwestern Japan.
“There have been many studies on Paleolithic migrations to Australia and its neighboring landmasses, often discussing whether these journeys were accidental or intentional,” said Kaifu. “Our study looks specifically at the migration to the Ryukyu Islands, because it is not just historically significant, but is also very difficult to get there. The destination can be seen from the top of a coastal mountain in Taiwan, but not from the coast. In addition, it is on the opposite side of the Kuroshio, one of the strongest currents in the world. If they crossed this sea deliberately, it must have been a bold act of exploration.”
This issue of the intentionality of this journey is less straightforward to solve than you might imagine. To investigate the likelihood of the journey occurring by chance, the effect of the Kuroshio on drifting craft needed measuring. To do this, Kaifu and his team used 138 satellite-tracked buoys to trace the path of a would-be drifter caught on this journey.
“The results were clearer than I would have expected,” said Kaifu. “Only four of the buoys came within 20 kilometers of any of the Ryukyu Islands, and all of these were due to adverse weather conditions. If you were an ancient mariner, it’s very unlikely you would have set out on any kind of journey with such a storm on the horizon. What this tells us is that the Kuroshio directs drifters away from, rather than towards, the Ryukyu Islands; in other words, that region must have been actively navigated.”
You might wonder how we can be so sure the current itself is the same now as it was over 30,000 years ago. But existing evidence, including geological records, tell researchers that currents in the region have been stable for at least the last 100,000 years. As for the researchers’ confidence that Paleolithic voyagers would not dare face stormy conditions that might otherwise explain chance migrations, prior research suggests that these voyagers were groups including families, whose modern-day analogues do not take such risks.
“At the beginning, I had no idea how to demonstrate the intentionality of the sea crossings, but I was lucky enough to meet my co-authors in Taiwan, leading authorities of the Kuroshio, and came across the idea of using the tracking buoys,” said Kaifu. “Now, our results suggest the drift hypothesis for Paleolithic migration in this region is almost impossible. I believe we succeeded in making a strong argument that the ancient populations in question were not passengers of chance, but explorers.”
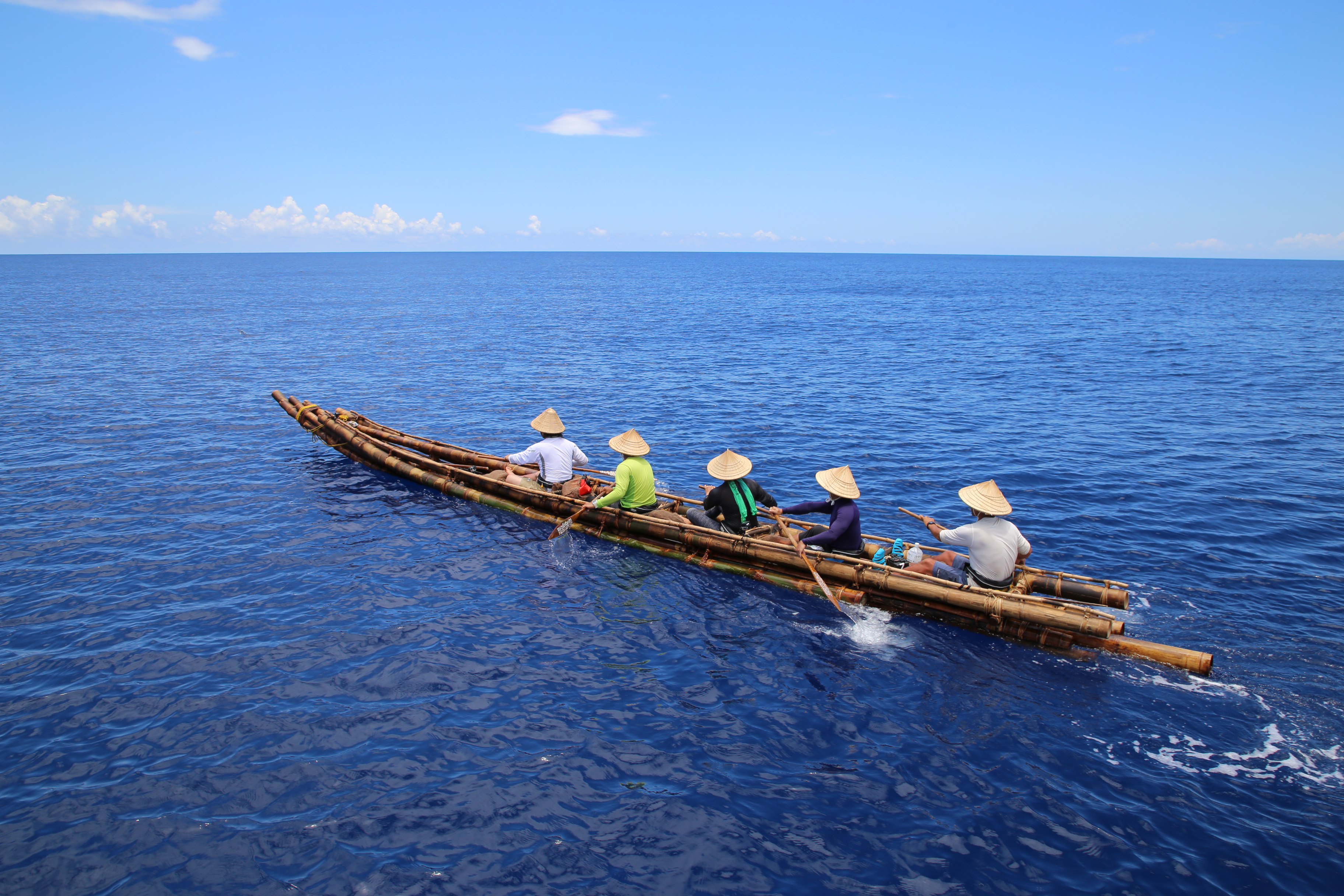

Bamboo raft. A candidate bamboo craft for the Ryukyu migration built for a re-enactment of that crossing. © 2020 Yosuke Kaifu
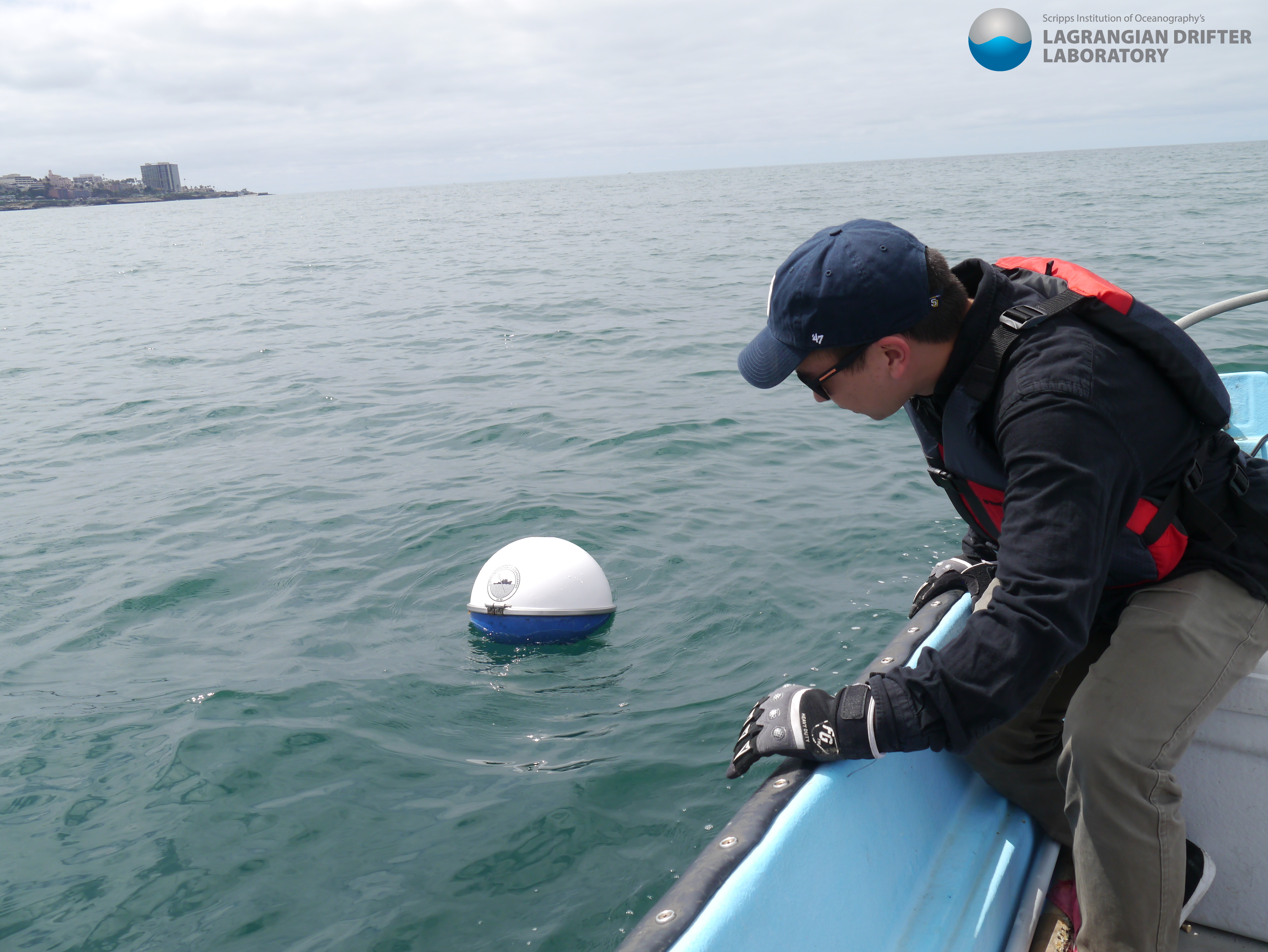

Buoy overboard. One of the satellite-tracking buoys. © 2020 Lagrangian Drifter Laboratory/University of California, San Diego
Papers
Kaifu, Y., Kuo, T.-H., Kubota, Y., Jan, S, "Palaeolithic voyage for invisible islands beyond the horizon," Scientific Reports: December 3, 2020, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-76831-7.
Link (Publication )
)
Related links
- Related research

- The University Museum at the University of Tokyo

- Holistic reenactment project of the voyage 30,000 years ago

- Lagrangian Drifter Laboratory