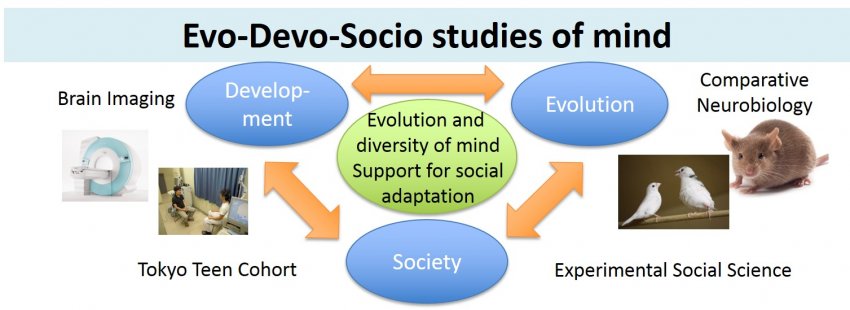
Evo-Devo-Socio Approach to the Mind


Kazuo Okanoya
Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
Professor
To integrate research and educational resources for human mind and behavior, we established Utokyo Institute for Diversity and Adaptation of Human Mind (Utidahm), Center for Integrative Science of Human Behavior (CiSHub), and Program for Human Integrative Science and Education of Mind (Phisem). At present, professors from eight departments participate in these programs. We propose to further integrate these programs to study Evo-Devo-Socio aspects of human mind and behavior.
Related links
Research collaborators
- Grad. Sch. Arts & Sciences: T. Hasegawa, Y. Yotsumoto, S. Koike
- Grad. Sch. Med Sci.: K. Kasai, Y. Kanoh
- Grad. Sch. Humanities & Sociology: T. Kameda
- Grad. Sch. Education: M. Nohchi
- Grad. Sch. Law & Politics. Sci.: J. Kato
- Grad. Sch. Science: K. Emoto
- Grad. Sch. Pharmaceutical Sci.: Y. Ikegaya
- Grad. Sch. Med Sci.: K. Kasai, Y. Kanoh
- Grad. Sch. Humanities & Sociology: T. Kameda
- Grad. Sch. Education: M. Nohchi
- Grad. Sch. Law & Politics. Sci.: J. Kato
- Grad. Sch. Science: K. Emoto
- Grad. Sch. Pharmaceutical Sci.: Y. Ikegaya
Related publications
- Evolution:Yuki, S., & Okanoya, K. (2017). Rats show adaptive choice in a metacognitive task with high uncertainty. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Learning and Cognition, 43(1), 109.
- Development:Koike, S., Barnett, J., Jones, P. B., & Richards, M. (2017). Cognitive profiles in childhood and adolescence differ between adult psychotic and affective symptoms: a prospective birth cohort study. Psychological Medicine, 1-12.
- Society:Kameda, T., Inukai, K., Higuchi, S., Ogawa, A., Kim, H., Matsuda, T., & Sakagami, M. (2016). Rawlsian maximin rule operates as a common cognitive anchor in distributive justice and risky decisions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 201602641.
- Development:Koike, S., Barnett, J., Jones, P. B., & Richards, M. (2017). Cognitive profiles in childhood and adolescence differ between adult psychotic and affective symptoms: a prospective birth cohort study. Psychological Medicine, 1-12.
- Society:Kameda, T., Inukai, K., Higuchi, S., Ogawa, A., Kim, H., Matsuda, T., & Sakagami, M. (2016). Rawlsian maximin rule operates as a common cognitive anchor in distributive justice and risky decisions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 201602641.
Contact
- Kazuo Okanoya