Implementable optimal resource allocation and stopping theory in stochastic numerical analysis


- 1.1 Mathematics
- 3.2 Mathematical and physical sciences
- 3.3 Engineering
- 3.8 Informatics
Reiichiro Kawai
Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
Professor
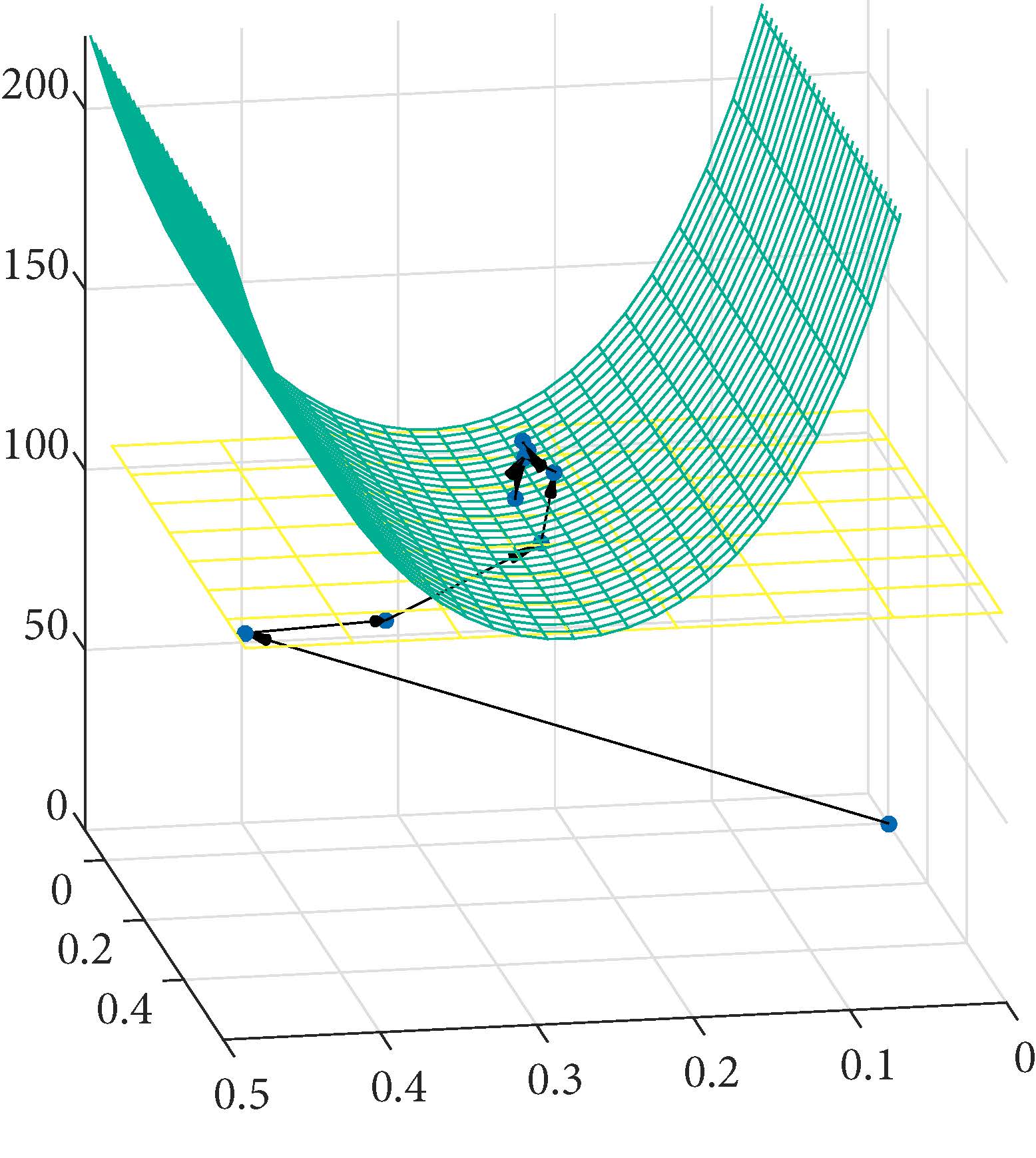
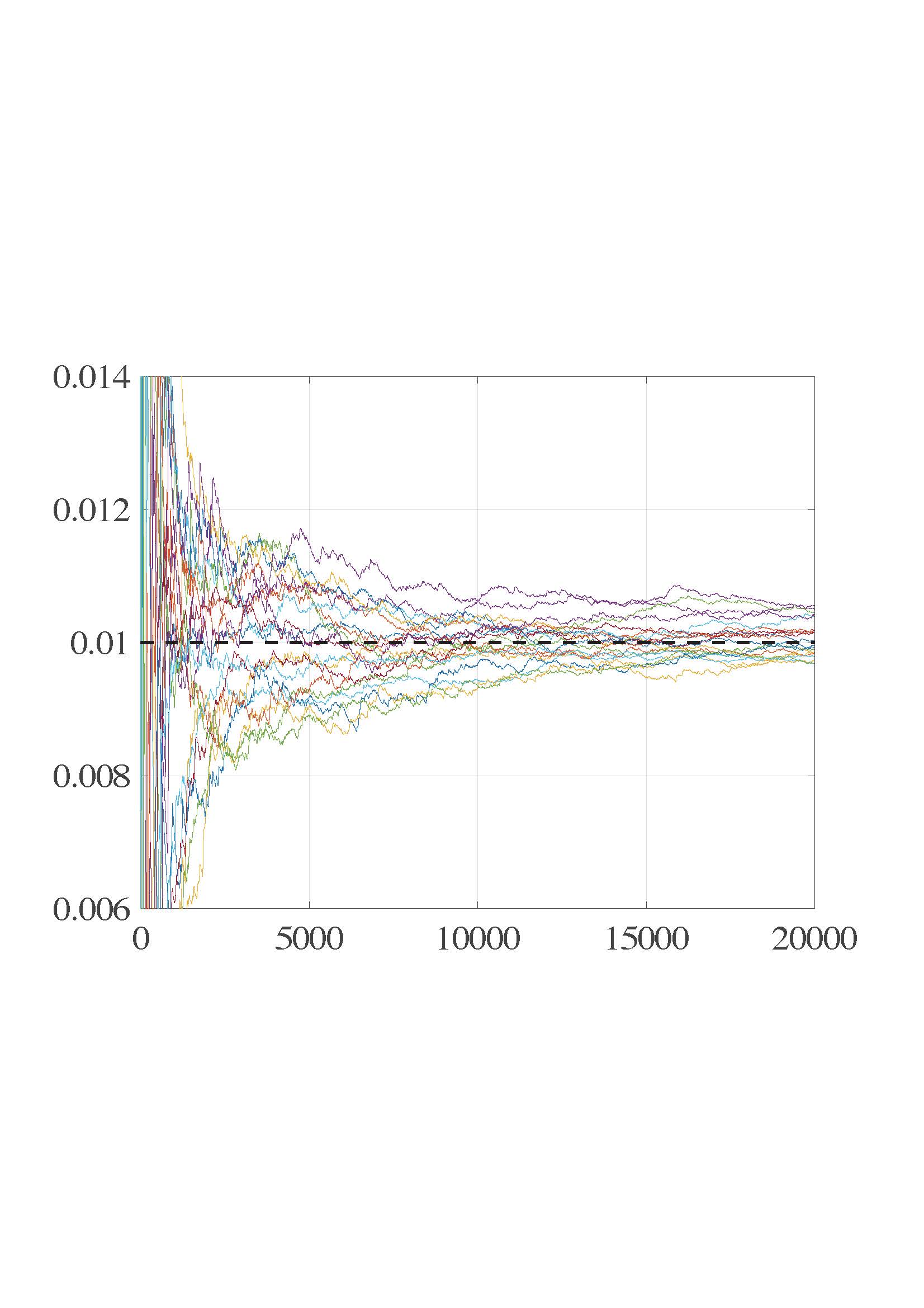
Probabilistic models, undoubtedly one of the most essential building blocks of AI implementation, have become increasingly prominent and significantly more complex in terms of the sheer need for intensive iterative computing; it could not be more urgent to design, devise and implement such demanding probabilistic models on a computer in a more efficient – and, ideally, optimal – manner. This project, thus, aims to establish and improve the fundamental theories on computing resource allocation , the optimal stopping of iteration, and convergence and error analyses for stochastic numerical methods, all with a clear view towards practical implementations.
Related links
Related publications
- Kawai, R., Acceleration on adaptive importance sampling with sample average approximation, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing (2017) 39(4) A1586-A1615.
- Kawai, R., Optimizing adaptive importance sampling by stochastic approximation, SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing (2018) 40(4) A2774-A2800.
SDGs
Contact
- Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- Tel: +81-3-5454-6475
- Email: raykawai[at]g.ecc.u-tokyo.ac.jp
※[at]=@