Meiji Period (1868-1912)

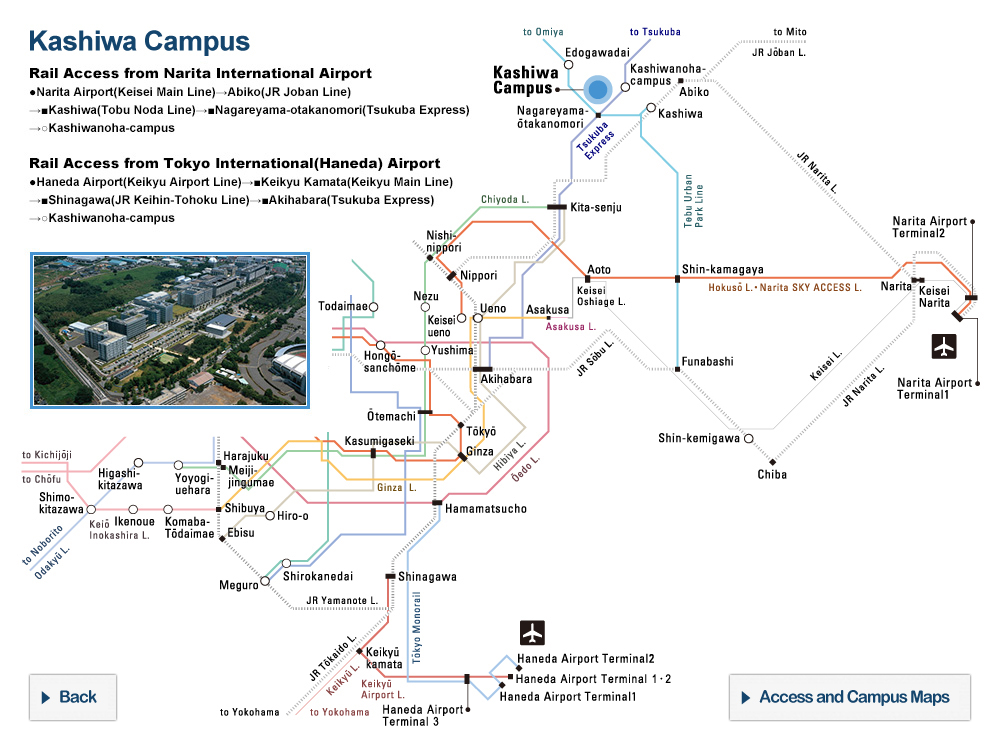
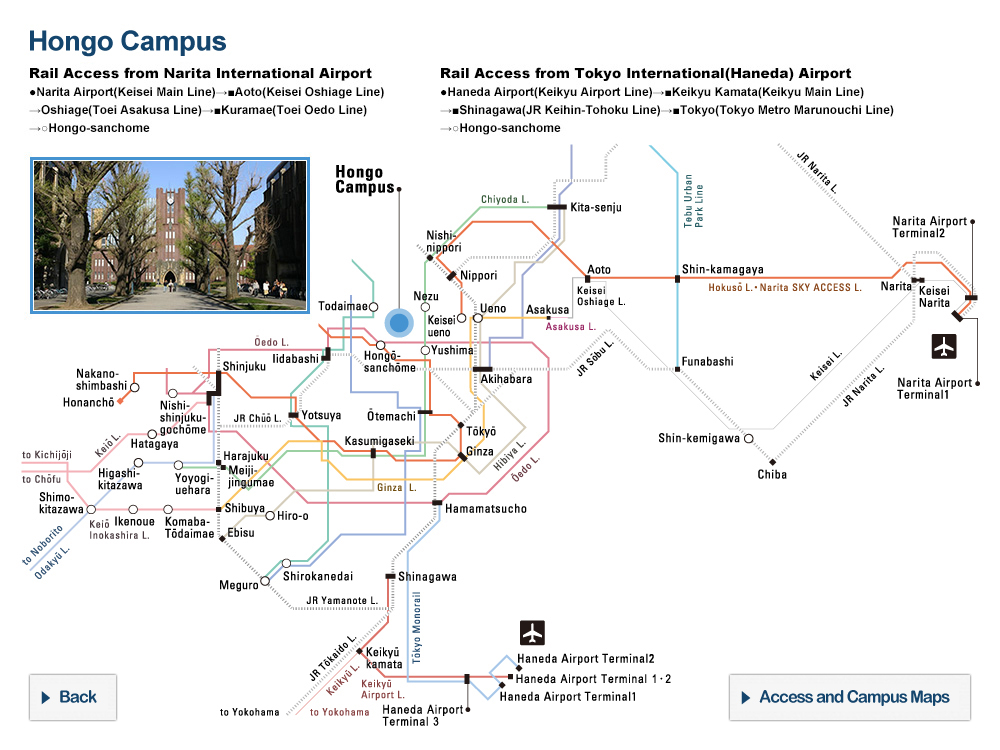
| 1876 | Tokyo Igakko transferred to Hongo, the present location of the University |
| 1877 | The University established as Tokyo Daigaku consisting of four departments: Law, Science, Literature and Medicine, and incorporating three institutions: Shoheiko (Japanese and Chinese Literature, established 1789), Yogakusho (Occidental Studies, established 1855) and Shutosho (Vaccinations, established 1860) |
| 1886 | The name of Tokyo Daigaku (Tokyo University) changed to Teikoku Daigaku (Imperial University) Absorbed Kobu Daigakko (Engineering College), resulting in five departments |
| 1890 | Established Tokyo Norin Gakko (Agriculture and Dendrology College), resulting in six colleges |
| 1897 | Name changed to Tokyo Teikoku Daigaku (Tokyo Imperial University) to distinguish it from the institution founded at this time in Kyoto |
Taisho Period (1912-1926)

Completion Ceremony, 1924
| 1916 | Institute for Infectious Diseases added |
| 1919 | Colleges became known as Faculties by virtue of Imperial Ordinance Faculty of Economics established, resulting in seven Faculties |
| 1921 | Aeronautical Research Institute established Tokyo Astronomical Observatory established |
Showa Period (1926-1989)

Field Stadium, c. 1935
| 1942 | Second Faculty of Engineering instituted (continued until 1951) |
| 1946 | Postwar expansion affecting the University Hospital, Branch Hospital, Marine Biological Station, Botanical Gardens, University Forests, Experimental Farm, Fisheries Laboratory, Engineering Research Institute, etc. Institute of Social Science established |
| 1947 | School Education Law promulgated Co-education introduced Name of the University changed from Tokyo Teikoku Daigaku to Tokyo Daigaku (The University of Tokyo) |
| 1949 | Former University Ordinance and other related laws repealed; under new School Education Law Tokyo Daigaku incorporated former Tokyo Imperial University and attached Medical College; reorganized on a four-year undergraduate basis with the exception of a six-year program for Medicine College of General Education formed amalgamating Daiichi Koto Gakko and Tokyo Koto Gakko and offering general education to all freshmen and sophomore degree candidates; First matriculation of College of General Education under new system took place in July Faculty of Education evolved out of the Faculty of Letters resulting in nine faculties Earthquake Research Institute added Institute for Oriental Culture established Institute of Industrial Science established Institute of Social Science established Institute of Journalism opened |
| 1950 | Historiographical Institute established |
| 1953 | Prototype of present graduate system comprising five graduate schools inaugurated (continued until March 1963) Institute of Applied Microbiology and Cosmic Ray Laboratory established |
| 1955 | Institute for Nuclear Study established |
| 1957 | Institute for Solid State Physics established |
| 1962 | Ocean Research Institute established |
| 1963 | Graduate School system reorganized to comprise eight graduate schools |
| 1965 | Graduate School system reorganized to comprise ten graduate schools |
| 1966 | University Museum, Computer Centre and Health Centre established |
| 1967 | Cryogenic Center established Name of Institute for Infectious Disease changed to Institute of Medical Science |
| 1970 | Radioisotope Center (currently the Isotope Science Center) established |
| 1972 | Research Center for Nuclear Science and Technology established Educational Computer Center established |
| 1975 | Environmental Science Center established |
| 1981 | Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science transferred Institute of Interdisciplinary Research established |
| 1983 | Laboratory of Molecular Genetics established Name of Research Center for Library and Information Science changed to Center for Bibliographic Information |
| 1985 | Japanese Language Center for Foreign Students established |
| 1986 | Center for Bibliographic Information transferred |
| 1987 | Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology established |
| 1988 | Tokyo Astronomical Observatory transferred Institute of Interdisciplinary Research abolished |
Heisei Period (1989-2019)

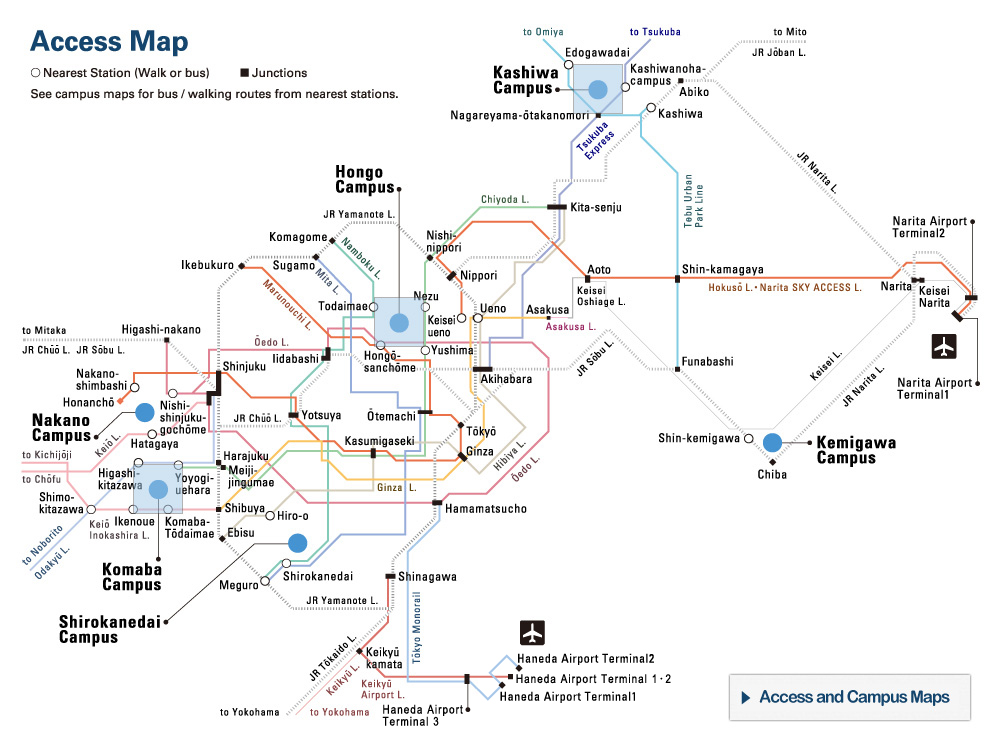
Kashiwa Campus (established in 1998)
| 1990 | Name of the Japanese Language Center for Foreign Students changed to the International Center |
| 1991 | Center for Climate System Research established |
| 1992 | Division of Mathematical Sciences became an independent division to result in twelve graduate schools within the Graduate School system The name of the Institute of Journalism and Communication Studies changed to the Institute of Socio-Information and Communication Studies Research into Artifacts, Center for Engineering established |
| 1993 | Name of Institute of Applied Microbiology changed to Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences Biotechnology Research Center established |
| 1994 | International Center for Elementary Particle Physics established Name of the Graduate School of Agricultural Sciences changed to the Graduate School of Agricultural and Life Sciences |
| 1995 | Asian Natural Environmental Science Center established Division of Sociology abolished Division of Humanities restructured and renamed the Graduate School of Humanities and Sociology |
| 1996 | Structure of the University Museum changed Center for Research and Development of Higher Education established Center for Collaborative Research established VLSI Design and Education Center established Administration Bureau unified with Student Affairs Department (Research Management and International Affairs Department established, and General Affairs Department's Japanese name changed) |
| 1997 | Institute for Nuclear Study abolished (and changed to High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, a facility open to all scholars in Japan) The process of placing emphasis on graduate school completed |
| 1998 | Graduate School of Frontier Sciences established Komaba Open Laboratory established Center for Spatial Information Science established |
| 1999 | Research Center for Advanced Economic Engineering established High Temperature Plasma Center established Name of Educational Computer Centre and Computer Centre changed to Information Technology Center |
| 2000 | Interfaculty Initiative in Information Studies established Graduate School of Interdisciplinary Information Studies established International Research Center for Medical Education established Institute for Cosmic Ray Research and Institute for Solid State Physics moved to the Kashiwa Campus |
| 2001 | Branch Hospital merged into the University Hospital Graduate School of Information Science and Technology established Institute of Industrial Science relocation to the Komaba Campus completed |
| 2002 | School of Nursing and School of Midwives closed Professor Emeritus Masatoshi Koshiba awarded the 2002 Nobel Prize for Physics |
| 2003 | Animal Center for Biomedical Research abolished Center for Disease Biology and Integrative Medicine established The Charter of The University of Tokyo enacted |
| 2004 | All National Universities transformed into National University Corporations; The University of Tokyo incorporated as a National University Corporation Graduate School of Public Policy established Institute of Socio-Information and Communication Studies abolished (became part of the Interfaculty Initiative in Information Studies/Graduate School of Interdisciplinary Information Studies) Research Center for Advanced Economic Engineering abolished (became part of the Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology) Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology changed into an Institution attached to the University |
| 2005 | Research Center for Nuclear Science and Technology abolished (became part of the Department of Nuclear Engineering and Management, the Graduate School of Engineering) The University of Tokyo Beijing Office established The University of Tokyo Action Plan published |
| 2007 | Todai-Yale Initiative established The University of Tokyo 130th anniversary celebrations |
| 2009 | Former Health Service Center abolished; Division of Health Service Promotion established |
| 2010 | Former International Center abolished; Division of International Affairs established (International Centers and the Center for Japanese Language Education) Ocean Research Institute and Center for Climate System Research reformed to establish the Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute Names of central administrative bodies changed to departments and groups |
| 2011 | The University of Tokyo Institutes for Advanced Study (UTIAS) established |
| 2012 | The University of Tokyo India Office established in Bangalore |
| 2013 | UTokyo Policy Alternatives Research Institute established as a University-wide center |
| 2015 | Professor Takaaki Kajita wins the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physics The University of Tokyo's action plan Vision 2020 published The University of Tokyo India Office relocated to New Delhi |
| 2016 | Center for Research and Development on Transition from Secondary to Higher Education established |
| 2017 | UTokyo named as a Designated National University |
| 2018 | Division of International Affairs reformed to establish the Division for Global Campus Initiatives |
Reiwa Period (2019-)

| 2021 | “UTokyo Compass” released |
| 2022 | The University of Tokyo Pandemic preparedness, Infection and Advanced research Center (UTOPIA) established |
| 2023 | Center for Global Education established |
| 2024 | UTokyo Center for Coproduction of Inclusion, Diversity and Equity established; Management Policy Council established |
| 2025 | Center for Strategic Promotion of GX established |